There are many types of capacitor but they can be split into two groups, polarized and unpolarized. Each group has its own circuit symbol.
Polarised capacitors (large values, 1µF +)
Examples:
Circuit symbol:

Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized and they must be connected the correct way round, at least one of their leads will be marked + or -. They are not damaged by heat when soldering.
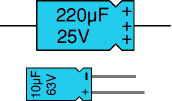
There are two designs of electrolytic capacitors; axial where the leads are attached to each end (220µF in picture) and radial where both leads are at the same end (10µF in picture). Radial capacitors tend to be a little smaller and they stand upright on the circuit board.
Related Articles:
It is easy to find the value of electrolytic capacitors because they are clearly printed with their capacitance and voltage rating. The voltage rating can be quite low (6V for example) and it should always be checked when selecting an electrolytic capacitor. If the project parts list does not specify a voltage, choose a capacitor with a rating which is greater than the project’s power supply voltage. 25V is a sensible minimum for most battery circuits.
Tantalum Bead Capacitors
Tantalum bead capacitors are polarized and have low voltage ratings like electrolytic capacitors. They are expensive but very small, so they are used where a large capacitance is needed in a small size.
Unpolarised capacitors (small values, up to 1µF)
Examples:

Circuit symbol:
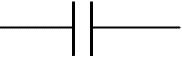
Small value capacitors are unpolarized and may be connected either way round. They are not damaged by heat when soldering, except for one unusual type (polystyrene). They have high voltage ratings of at least 50V, usually 250V or so. It can be difficult to find the values of these small capacitors because there are many types of them and several different labeling systems!

Many small value capacitors have their value printed but without a multiplier, so you need to use experience to work out what the multiplier should be!
For example 0.1 means 0.1µF = 100nF.
Polystyrene Capacitors
This type is rarely used now. Their value (in pF) is normally printed without units. Polystyrene capacitors can be damaged by heat when soldering (it melts the polystyrene!) so you should use a heat sink (such as a crocodile clip). Clip the heat sink to the lead between the capacitor and the joint.

Variable capacitors
Variable capacitors are mostly used in radio tuning circuits and they are sometimes called ‘tuning capacitors’. They have very small capacitance values, typically between 100pF and 500pF (100pF = 0.0001µF). The type illustrated usually has trimmers built in (for making small adjustments – see below) as well as the main variable capacitor.
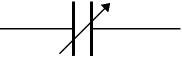
Trimmer capacitors
Trimmer capacitors (trimmers) are miniature variable capacitors. They are designed to be mounted directly onto the circuit board and adjusted only when the circuit is built.
Trimmer Capacitors Symbol:
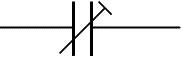
Trimmer Capacitor Photograph:

Related Articles: